Introduction
Boolean operators can be used to construct very specific queries. They are named after the nineteenth-century mathematician George Boole. The three Boolean operators are: OR, AND, and NOT.
OR
It is advised to use synonyms of your search term in your query. This is important when you know synonyms are often used or when you want to find as much as possible on a specific topic.
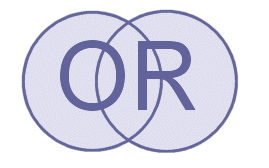
To search for all the synonyms or related terms of one concept in one go, you can use the Boolean operator OR to combine the terms. In this case you will find references containing any or all of the terms that are being OR-ed together.
If you are looking for references on pigs, for example, you may want to search with the terms pig, pigs and swine. Using the Boolean operator OR, this makes: pig OR pigs OR swine Now, you will end up with a larger set of references than if you had used only one of the terms.
AND
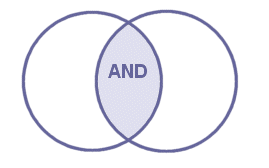
Most search queries consist of two or more concepts, e.g. the influence of housing of pigs on meat quality. You will possibly find relevant information if you search for all the concepts separately, but your search will be more effective if you combine at least two of the concepts with the Boolean operator AND.
Combination of terms with the AND operator narrows down your search to only those references containing all of the terms. So, if you perform the search: pigs AND housing AND meat quality you will end up with a smaller set of results than if you search for a single concept.
NOT
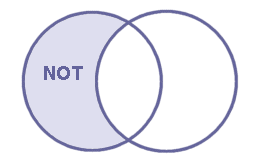
The third Boolean operator is NOT. This operator is used when you want to make sure that a concept is not included in the results of your search in order to reduce the number of references you have retrieved.
When you use NOT in your search, e.g. pigs NOT cows, you have to be aware that you may also exclude references about both pigs and cows that you want to read. So, the operator NOT requires a careful usage.
In some databases AND NOT or ANDNOT is used.
Combining boolean operators
Boolean operators can be used in all combinations in your search query, but mind the order in which you place them. Boolean operators are processed in the following order: NOT, AND, and OR. By way of exception Google and the database Scopus use another order of precedence: OR, AND, NOT. To be sure that the search is performed as you intended it to be, use parentheses to separate your search terms. Examples of good combinations are:
- obesity AND children AND Europe
- obesity AND (Netherlands OR Belgium)
- (pigs OR swine) AND housing
- pigs AND housing NOT 2005
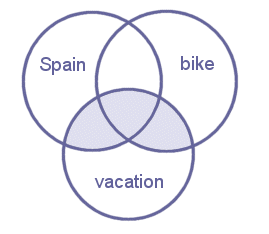
- (vacation NOT bike) AND Spain
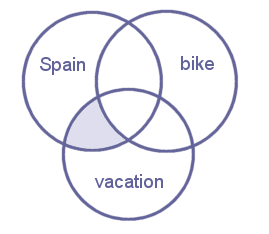
- vacation NOT (bike AND Spain)
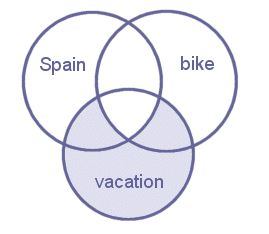
- vacation AND (bike OR Spain)